PON, GPON, XG-PON, 10G-EPON… What does this mean?
PON stands for “Passive Optical Network”, in reference to the topography of fiber networks, made up of non-active elements from the point of origin (network head) to the end points (subscribers or customers). The other acronyms refer to the transmission standards broadcast in the physical network. How are they different from each other? Can they be analyzed using a PROLITE-67?
PON ARCHITECTURE: THE PHYSICAL LAYER
PON is the network architecture used for the deployment of Fiber To The Home (FTTH) services. As stated, it is made up of passive elements: Fiber optics, multiplexers, couplers, connectors, etc.
The backbone of a fiber optic network starts from the network head and is divided through the couplers, thus creating different branches which communicate in two directions on the network, the branches not communicating with each other.
The downstream bandwidth of the headend is shared with all users and the signal is of constant power.
The upstream bandwidth from users to the head end is shared and transmitted in burst mode: a time window is granted for each subscriber. This mode is called TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access).
The PROLITE-67 optical analyzer detects and indicates whether the signal is transmitted in burst mode. In this way we can certify that the upstream channel operates in TDMA mode.
TRANSMISSION STANDARDS FOR PON NETWORK
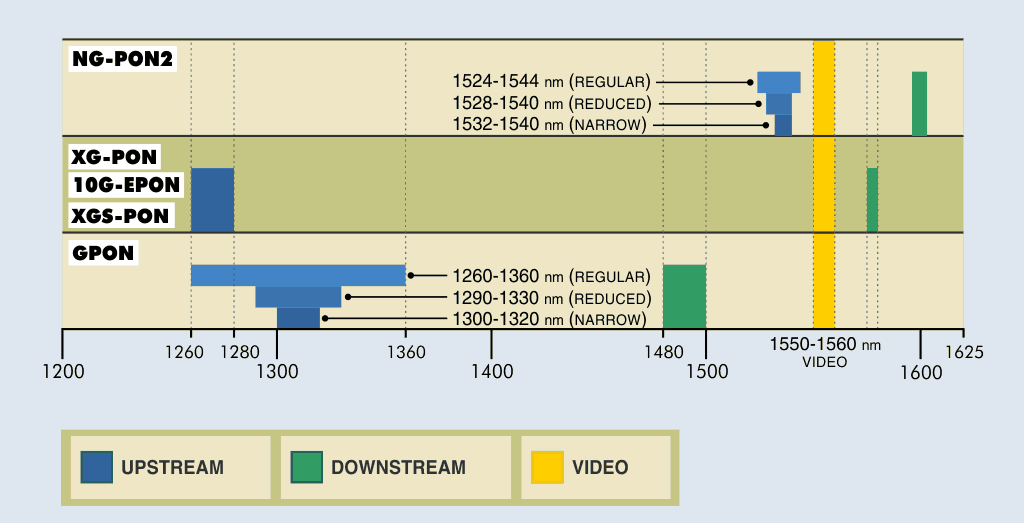
Each transmission standard uses its own wavelength range. To follow the evolutions, we try to guarantee backward compatibility with the previous standards by using the wavelengths available in the optical spectrum, and not yet used by the previous standards.
|
|
GPON |
XG-PON |
XGS-PON |
NG-PON2 |
|
Upstream (nm) |
1260-1360 |
1260-1280 |
1260-1280 |
1524-1544 |
|
Downstream (nm) |
1480-1500 |
1575-1580 |
1575-1580 |
1596-1603 |
|
Video (nm) |
1530-1565 |
1530-1565 |
- |
- |
|
Upload (Gbps) |
1,2 |
2,5 / 10 |
10 |
40 |
|
Download (Gbps) |
2,5 |
10 |
10 |
40 |
Let's go back to the three main standards, from the oldest to the most recent:
XG-GPON is also called 10G-EPON.
Have you noticed? The downstream channels of the GPON, XG-EPON and XGS-PON
standards share a certain wavelength range (from 1260 to 1280 nm). This is
possible because, although reserved for GPON, this band is not used and XG-PON /
XGS-PON was able to take advantage of this free band.